Ultrasound B-Scan
Teaching the basics of the B-mode technique by taking the ultrasound cross-sectional image of a simple test object “by hand” using an ultrasound echoscope
By taking an ultrasound cross-sectional image of a simple test object “by hand” using an ultrasound echoscope, the basics of the B-scan method are clearly explained. Special features of the image quality such as sound focus, spatial resolution or imaging errors are examined and analyzed.
Keywords: speed of sound, reflection, transmission, reflection coefficient, ultrasound echography, A-image, grayscale representation, B-image, lateral resolution, focal zone, image artifacts
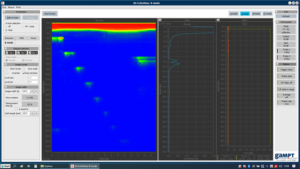
The conversion of the amplitude values of an A-scan into gray or color values and the representation of the transit time as penetration depth produces a line of points with different brightness or color values. The juxtaposition of such adjacent depth scans of an ultrasound probe that is guided along a line over the examination area produces a cross-sectional image, the so-called B-image. The location along this line is determined from the position of the probe and its speed of movement. A simple form of B-image acquisition is the slow guidance of the ultrasound probe by hand (compound scan). The image quality depends on the coordinate-accurate image point transfer, the axial and lateral resolution of the ultrasound probe, the gray value or color value resolution, the number of lines and imaging errors. In order to achieve an exact lateral resolution, for example, an additional coordinate acquisition system such as a linear scanner is required.
The screenshot of the measurement software shows the B-image of the examination of a test body with defined built-in defects. Manual scanning of the body makes the functionality of the B-image method clearly "understandable". Mechanical scanning (PHY16) can reduce the problems of movement artifacts caused "by hand" with regard to lateral resolution.
SCOPE OF DELIVERY:
| Item No. | Designation |
|---|---|
| 10400 | Ultrasonic echoscope GS200 |
| 10151 | Ultrasonic probe 1 MHz |
| 10152 | Ultrasonic probe 2 MHz |
| 10201 | Test block (transparent) |
| 10204 | – optional: test block (black) |
| 70200 | Ultrasound gel |
ADDITIONAL EXPERIMENTS: