Transverse Waves in Solids
Investigation of the generation and propagation of longitudinal and transverse sound waves in solids using ultrasound transmission through a plane-parallel plate at different angles of incidence
The generation and propagation of longitudinal and transverse sound waves in solids is investigated using ultrasound transmission through a plane-parallel plate at different angles of incidence. The elastic material parameters such as elastic and shear modulus and Poisson's ratio for the plate materials used are derived from the determined longitudinal and transverse sound velocities.
Keywords: Ultrasound propagation in solids, transmission, reflection, longitudinal and transverse waves and sound velocities, elastic modulus, shear modulus, Poisson's ratio
In contrast to gases and liquids, solids can excite not only longitudinal but also transverse waves due to their elastic material properties. When passing through a plane-parallel plate, longitudinal and/or transverse waves are excited depending on the angle of incidence of the sound. The angles of total reflection for the longitudinal and transverse waves as well as the angle at which the transverse wave reaches its maximum correspond to the respective speed of sound. By recording the amplitudes of the longitudinal and transverse transmission signals over a corresponding range of the angle of incidence, these angles can be determined and the associated speeds of sound determined. The elastic material properties of the plate materials used, such as elasticity and shear modulus as well as the Poisson ratio, can be calculated from the speeds of sound.
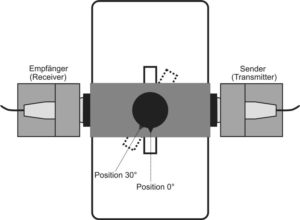
Schematic views of the measurement setup
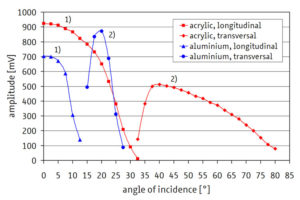
Measurement curves
The graphic shows the amplitude-angle curves for determining the angles for total reflection (longitudinal and transverse) and the maximum amplitude (transverse). Regardless of the material but for different angles, the amplitude-angle dependence of the transmission can always be described by three areas: only longitudinal signal (1), a mixed mode of longitudinal and transverse signal and only transverse signal (2).
SCOPE OF DELIVERY:
| Item No. | Designation |
|---|---|
| 10400 | Ultrasonic echoscope GS200 |
| 10151 | 2 ultrasonic probes 1 MHz |
| 10218 | Transverse wave set |
| 70200 | Ultrasound gel |
ADDITIONAL EXPERIMENTS:
| PHY20 | Determination of the focus zone |
| IND06 | Angle head testing |
| IND08 | Defect testing |
| MED02 | Ultrasound examinations on the breast model (mammography) |



