Sound Attenuation in Liquids
Investigation of the attenuation of sound waves in different liquids depending on the sound path
The experiment examines the attenuation of sound waves in various liquids as a function of the sound path. The sound attenuation coefficient is determined for each of the liquids using linear regression.
Keywords: Sound propagation in liquids, longitudinal waves, reflection, absorption, scattering, sound attenuation in liquids, attenuation coefficient
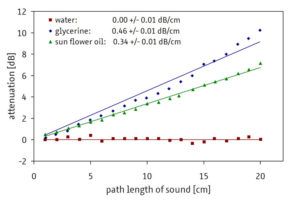
In gases and liquids, sound propagates in the form of longitudinal waves. The sound waves can lose energy on their way through the liquid through absorption, reflection or scattering. The sound field geometry can also influence the sound attenuation. In the experiment, the amplitudes of the reflection echoes are measured by an easily movable aluminum sound reflector. By moving the reflector in the liquid under investigation, the amplitude values for a large number of different sound paths can be quickly determined using the pulse-echo method. The attenuation or damping of the signal amplitude A can be described by the general attenuation law A = A 0 e -ax . For two different sound paths x 1 and x 2, the following linearized form results: 2 Ln(A 2 /A 1 ) = a (x 1 – x 2 ). The attenuation coefficient a of the respective liquid can thus be determined by linear regression over the measuring points in the attenuation-sound path diagram.
In the experiment, the sound attenuation in water, a commercially available sunflower oil and glycerine (86.5%) was examined as an example. The diagram shows the measured values with the regression lines for determining the sound attenuation coefficients a. At the frequency used of 2 MHz, the measurement with water shows no measurable attenuation, so that the influence of the sound field geometry for the measurements in the experiment
SCOPE OF DELIVERY:
| Item No. | Designation |
|---|---|
| 10400 | Ultrasonic echoscope GS200 |
| 10152 | 2 ultrasonic probes 2 MHz |
| 10218 | Transverse wave set |
| 70200 | Ultrasound gel |
ADDITIONAL EXPERIMENTS:
| PHY01 | Basics of ultrasound echography (A-scan) |
| PHY02 | Speed of sound in solids |
| PHY03 | Sound attenuation in solids |
| PHY19 | Phase and group velocity |