HO-ED-INT-10 Fabry - Perot Interferometer Projection Based
Couldn't load pickup availability
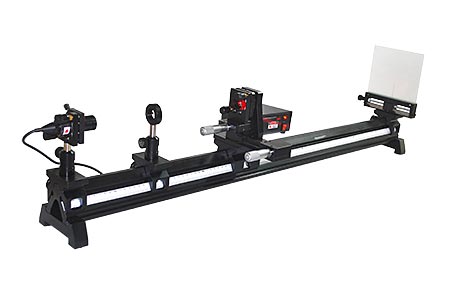
Fabry - Perot Interferometer
Projection Based
In Fabry - Perot interferometer, the distance between the partially reflecting mirrors are varied by using coarse and finely adjustable translation stage driven by micro-meters. One beam splitter is fixed and the other is mounted on the translation stage through a kinematic mount. This two axis kinematic mount is used to correct the parallelism between beamsplitters.
The Fabry - Perot design contains plane surfaces that are partially reflecting so that multiple rays of light are responsible for the creation of the observed interference patterns. For high resolution spectroscopy, where a resolution in the range of MHz to GHz is required, a Fabry - Perot interferometer (FP) is used. The FP consists of two plane mirrors mounted accurately parallel to each another, with an optical spacing of 'd' between them.
The enclosed air gap generally varies from several millimeters to centimeters, when the device is used interferometrically. If the gap can be mechanically varied by moving one of the beam splitters, then the device is referred to as an interferometer. It’s transmission spectrum as a function of wavelength exhibits peaks of transmission corresponding to resonances of the etalon. Fabry - Perot interferometers are widely used in telecommunication, lasers and spectroscopy for controlling and measuring the wavelength of light.
Experiment:
To find the wavelength of monochromatic light
The wavelength of laser is calculated by,
λ = ( 2d / N ) Δ
where ‘d’ is the change in position that occurs for ‘N’ fringes to pass and Δ is the calibration constant of the micrometer
To determine the spacing between the plates of fabry perot etalon from the fringe Pattern
The Spacing of the Etalon is given by,
t = nD2λ / χn2
where n is the order, ‘D ’ is the distance between the etalon and the screen, ‘λ’ is the wavelength of light used.
χn2 = χm+n2 - χm2
χm+n2 is the square of the radius of (m+n)th ring and χm2 that of mth ring.
To find the finesse and free spectral range (FSR) of etalon from the fringe calibration at different cavity thickness
The Free Spectral Range of the Etalon is given by,
FSR = c / 2t,
Where c is the speed of light in air and t is the spacing of the Etalon
The finesse is a measure of the interferometer's ability to resolve closely spaced spectral lines.
The finesse F is defined by the following equation.
F = π √R / ( 1-R )
Where, R is the reflectivity of surfaces
Features:
| Diode laser is used as the light source. |
| The mechanical assembly is made out of corrosion free materials. |
| All components and modules are mounted on rail by carriage system for easy adjustment. |
| The optics and mechanics used are of research quality. |
Drawings:

Schematic Diagram:

Related Topics:
Fabry - Perot Interferometer - Spectral Range
If two wavelengths are very close, their fringe maxima may overlap
The two peaks will be distinguishable if the two wavelengths are too close
A separation of full width at half maximum (FWHM) corresponds to minimum separation between the wavelength components
Scope of Delivery:
Allen Key
Instruction Manual